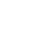The Lifesaving Marvel: Ventilators in Healthcare
Ventilators are indispensable devices in the realm of healthcare, playing a critical role in supporting patients with respiratory distress. These sophisticated machines, also known as mechanical ventilators, assist individuals in breathing when their natural respiratory function is compromised. From intensive care units to emergency rooms, ventilators have become a cornerstone in the treatment of various medical conditions.
Understanding Ventilators:
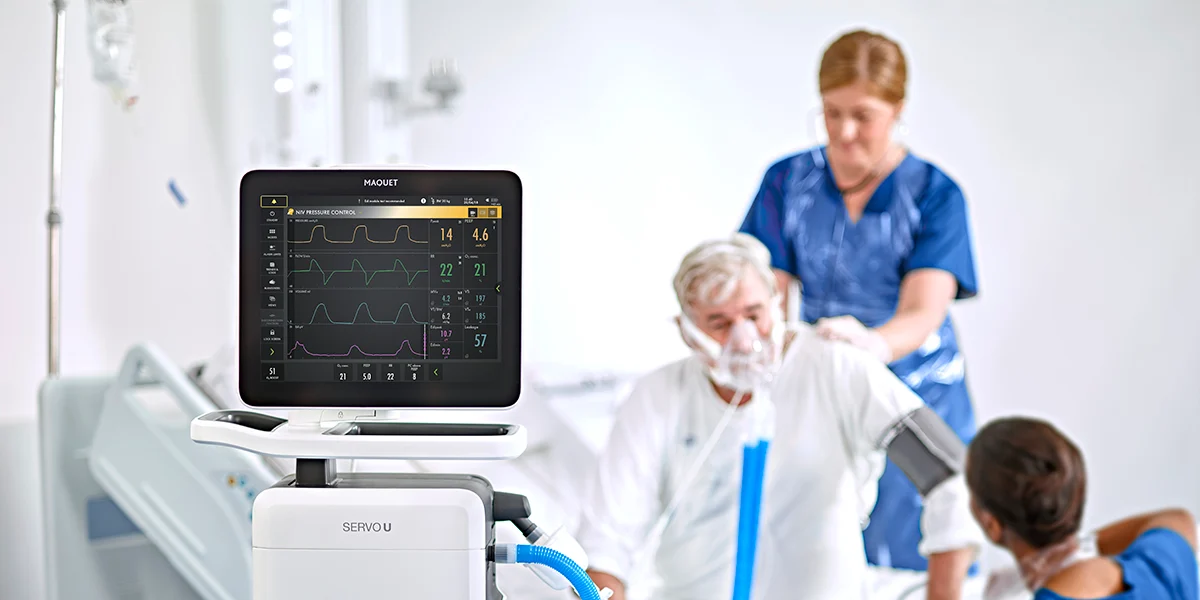
- Definition and Functionality: Ventilators are mechanical devices designed to deliver breathable air into and out of the lungs, providing vital respiratory support. They operate by simulating the natural breathing process through a controlled mechanism.
- Components: Explore the intricate components that make up a ventilator, including the ventilator circuit, control system, and the patient interface.
Types of Ventilators:
- Invasive Ventilation: Discuss the conventional approach involving endotracheal intubation, where a tube is inserted into the patient’s trachea. Delve into the advantages and drawbacks of invasive ventilation.
- Non-Invasive Ventilation: Explore alternatives like BiPAP and CPAP, which provide respiratory assistance without the need for intubation. Highlight the scenarios where non-invasive ventilation is preferred.
Indications for Ventilator Use:
- Respiratory Failure: Understand how ventilators are employed in cases of respiratory failure caused by conditions such as pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Surgery and Anesthesia: Examine the role of ventilators in ensuring a patient’s respiratory stability during surgeries and while under anesthesia.
Challenges and Innovations:
- Resource Allocation: Explore the challenges associated with the availability and distribution of ventilators, especially during health crises such as pandemics.
- Technological Advancements: Highlight recent innovations in ventilator technology, including portable ventilators, smart ventilation algorithms, and remote monitoring capabilities.
COVID-19 and Ventilators:
- Impact of the Pandemic: Discuss the surge in demand for ventilators during the COVID-19 pandemic and the challenges faced by healthcare systems worldwide.
- Adaptations and Solutions: Explore how the medical community adapted to the increased demand, including innovations in ventilator design, repurposing existing devices, and global collaboration.
Ethical Considerations:
- End-of-life Decisions: Examine the ethical dilemmas surrounding the use of ventilators in end-of-life situations, especially when resources are limited.
- Patient Autonomy: Discuss the importance of respecting patients’ wishes regarding ventilation and the role of advanced directives in guiding medical decisions.
Training and Expertise:
- Healthcare Professionals: Highlight the importance of specialized training for healthcare professionals responsible for operating and managing ventilators. Discuss the role of respiratory therapists, nurses, and physicians in ensuring optimal ventilator performance and patient safety.
- Continuous Education: Emphasize the need for ongoing education and training to keep healthcare providers abreast of the latest developments in ventilator technology and best practices.
Future Trends:
- Telemedicine Integration: Explore the potential integration of ventilators with telemedicine platforms, enabling remote monitoring and adjustment of ventilator settings. Discuss the benefits in terms of patient care and resource optimization.
- Artificial Intelligence in Ventilation: Investigate the role of artificial intelligence in optimizing ventilator settings based on real-time patient data. Discuss how AI algorithms can enhance ventilation precision and efficiency.
Global Access to Ventilators:
- Disparities in Access: Address the global disparities in access to ventilators, focusing on challenges faced by low-income countries and efforts to bridge the gap.
- Humanitarian Initiatives: Highlight international efforts and partnerships aimed at providing ventilators to regions in need during emergencies and public health crises.
Environmental Considerations:
- Sustainability in Ventilator Design: Discuss the growing awareness of the environmental impact of medical devices, including ventilators. Explore initiatives to design more sustainable and eco-friendly ventilators without compromising performance.
- Medical Waste Management: Examine the challenges associated with the disposal of ventilators and related equipment, emphasizing the importance of environmentally responsible practices in healthcare.
Conclusion:
As ventilators continue to evolve, their impact on healthcare transcends the confines of hospital walls. The future promises further innovations, ethical considerations, and global initiatives to ensure equitable access to this life-saving technology. Ventilators, once confined to critical care units, have become a symbol of resilience, adaptability, and collaboration within the medical community. As we navigate the challenges of today and tomorrow, the role of ventilators in preserving life remains indispensable, reinforcing their status as a cornerstone of modern medicine.
Ventilators stand as a testament to human ingenuity in the face of medical challenges. From routine surgeries to global health crises, these devices continue to be a lifeline for patients in respiratory distress. As technology advances, and healthcare systems adapt, the role of ventilators in saving lives remains paramount, shaping the landscape of critical care in the 21st century.